(426 products available)




















 Ready to Ship
Ready to Ship


















































































































































































































A sensible heat exchanger is a device or equipment that transfers heat without changing the phase of the material. There are two common types of sensible heat exchangers: the plate heat exchanger and the shell and tube heat exchanger.
Plate heat exchanger
The plate heat exchanger is usually made of numerous thin plates. All plates are latched together to form several channels. In general, two fluids run through the channels. The fluids can be different liquids or gases. The corrugated heat transfer plates provide more surface area for efficient heat transfer. Working with its pump station, the plate heat exchanger regulates the temperature of the liquid and gases in the process. It is widely used in food processing, HVAC, refrigeration, and power generation industries. Advantageously, the plate heat exchanger has a higher heat transfer efficiency than shell-and-tube heat exchangers. Besides, it takes a small area.
Shell and tube heat exchanger
The shell and tube heat exchanger consists of numerous long tubes bundled together within a larger cylindrical shell. Usually, one fluid runs through the tubes, and the other fluid flows around them within the shell. The two fluids are separated by a solid wall so that they can exchange heat. The shell and tube heat exchanger can handle large heat transfer quantities. It is suitable for high heat transfer demands. Shell and tube heat exchangers are often found in oil refineries, chemical plants, power plants, and other heavy industrial applications. They are used to cool, heat, or condense fluids and gases. Compared with the plate heat exchanger, the shell and tube heat exchanger is more robust and suitable for harsh working environments.
Some specifications of heat exchangers are as follows:
Multiple types of heat exchangers require different maintenance methods. Here are some universal tips for taking care of heat exchangers.
The main applications of sensible heat exchangers are in air conditioning and refrigeration systems, where they change the temperature of air.
Continuous plate exchangers are mostly used for milk but can also be used in other industries. In the food industry, they heat fruit juices, soups, and other food products. In the chemical industry, they cool different chemicals and gasses. In the power industry, they are used in geothermal, solar and electric power plants. When water vapour in the air passes over a cool plate, it releases energy and condenses into water. This process is called dehumidification, and sensible heat exchangers in HVAC systems often use it to remove excess moisture from the air.
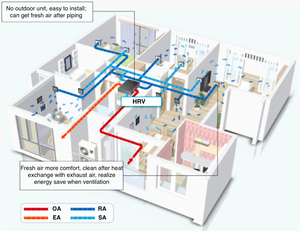
Sensible heat exchangers can also be found in heat recovery ventilators (HRVs) and enthalpy recovery ventilators (ERVs). These systems are used during the ventilation process to transfer heat from exhaust air to incoming fresh air. By doing so, they are able to reduce energy loss and maintain temperature levels inside a building. In residential settings HRVs are commonly used during the winter, while ERVs can be found in areas with high humidity.
A listed applicational example shows how versatile the device is:
Industrial
Sensible heat exchangers are essential in various manufacturing sectors to effectively control and optimise process temperatures. Their applications include pre-heating raw materials, tempering, drying, pasteurising, and cogeneration.
Marine
It is imperative that temperature control be injected into the design of marine systems to enhance the efficiency of energy usage and extend the lifespan of crucial machinery. Such marine systems include fresh water generators, marine desalination systems, marine compressor systems, propulsion systems, marine exhaust gas boilers, and marine energy recovery systems.
Power
Sensible heat exchangers play a crucial role in boosting energy generation within power plants by utilising residual heat from various processes. Their applications encompass gas and steam turbine systems, heat recovery steam generators, combined cycle power plants, ammonia systems, and gas turbine inlet air cooling.
Data Centres
In data centres, it is crucial to ensure the reliable operation of servers, safeguard against data loss, and maintain the availability of business services. Hence, the optimal temperature control and regulation of the data centre system is of utmost importance. This can be achieved through the implementation of sensible heat exchangers, which facilitate the efficient transfer of heat between different systems.
Indoor
Indoor heat exchangers are typically utilised in the construction and building sector, including offices, hotels, schools, shopping centres, apartments, hospitals, and other residential areas. These spaces necessitate the installation of indoor heat exchangers for the purposes of heating, cooling, and ventilation.
Identifying Installation Requirements:
Business buyers should first examine the installation requirements. They should check factors like the amount of place, pipe networks, and insulated bellows. Buyers need to ensure connections, compact design, and good extendable adaptability. A fit for the present HVAC system is vital for straightforward assembly and effective performance.
Different Types:
different types of heat exchangers work for specific applications. Plate heat exchangers suit compact spaces. Shell and tube ones work for industrial fields. Air-cooled ones reduce water use, and double-tube ones support safe applications. Choose models which fulfill needs and fit budgets.
Drying Purposes:
It is essential to select the fitting type of heat exchanger depending on the exact drying purpose. In particular, buyers need to consider the kind of material to be dried, the needed drying temperature, and the humidity. By evaluating these elements, buyers can choose a sensible heat exchanger that meets their distinct drying demands and achieves optimized drying efficiency.
Energy Efficiency:
Choose the heat exchanger that shows low energy losses and fit for a system to enhance energy efficiency. Also, heat recovery capability and average operating efficiency matter. A strong, sensible heat recovery system decreases energy consumption and brings substantial cost savings.
Maintaining Costs:
Consider the maintaining costs over the complete lifecycle. Heat exchanger models and types can give different maintenance and service expense needs. Select a heat exchanger that has reasonable maintenance costs, for it to be a sensible long-term investment.
Q: Which is more efficient, a sensible or latent heat exchanger?
A: Latent heat exchangers are generally more efficient than sensible heat exchangers because they can recover heat without a large temperature difference. They also transfer more energy in a given volume because they utilize phase change.
Q: When should one use a sensible heat exchanger?
A: One should consider using a sensible heat exchanger when the budget is tight, as these heat exchangers are more affordable. Also, consider using a sensible heat exchanger when the application can work with the temperature difference that a sensible heat exchanger requires. Lastly, it may be unnecessary to use a latent heat exchanger's complexity and efficiency, making sensible heat exchangers more suitable for some straightforward applications.
Q: Do sensible heat exchangers remove humidity?
A: No, it is the latent heat exchangers that remove humidity from the air.
Q: Can sensible heat exchangers be insulated?
A: Yes, but it is important to note that heat exchangers are maintained at high temperatures to avoid heat recovery. Therefore, it can be important to insulate them only if it does not compromise their heat transfer functions.