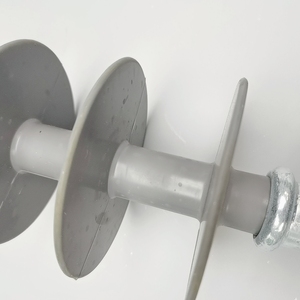
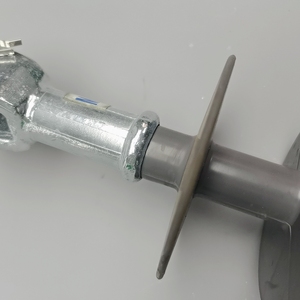
Introduction to Power Line Polymer Insulator
Power line polymer insulators are critical components in the electrical transmission and distribution landscape. Made from advanced materials, these insulators are designed to support power lines while providing electrical insulation. They are increasingly favored over traditional ceramic insulators due to their lightweight nature and exceptional performance in various environmental conditions. In this description, we will explore the types, features, and applications of power line polymer insulators, along with their advantages in modern electrical systems.
Types of Power Line Polymer Insulators
Power line polymer insulators are categorized into several types based on their design and functionality. Understanding these types can help in selecting the right insulator for your specific application:
- Suspension Insulators: Used primarily in overhead power lines, these insulators support the weight of the conductor while maintaining electrical insulation.
- Pin Insulators: Commonly utilized in lower voltage electrical lines, pin insulators securely hold the transmission wire at a single point.
- Strain Insulators: These are employed where the conductor is subjected to tension as they help to handle mechanical loads effectively.
- Line Post Insulators: Positioned along the line, they support the power line while allowing for easy maintenance and upgrades.
Features and Advantages of Power Line Polymer Insulators
Power line polymer insulators offer a variety of features that contribute to their effectiveness and longevity in the field:
- Lightweight Construction: The lightweight properties of polymer materials make these insulators easier to handle and install than traditional ceramic insulators.
- Excellent Weather Resistance: They perform exceptionally well under diverse weather conditions, from heavy rain to extreme temperatures, reducing the risk of failures.
- High Mechanical Strength: Polymer insulators boast impressive mechanical strength, which is vital for maintaining system integrity in harsh environments.
- Long Lifespan: Due to their resistance to environmental degradation, polymer insulators can last longer, reducing maintenance costs.
- Electrical Stability: They maintain superior electrical performance, ensuring minimal energy loss and high conductivity.
Applications of Power Line Polymer Insulators
Power line polymer insulators find diverse applications across various sectors, showcasing their versatility and robustness:
- High Voltage Transmission Lines: Essential for ensuring the reliability of electrical transmission over long distances.
- Distribution Networks: Widely used in urban and rural power distribution systems to maintain service continuity.
- Renewable Energy Systems: Employed in wind and solar power plants to support the power lines connecting to the grid.
- Railway Electrification: Utilized in overhead lines for electric trains, where lightweight and durable insulators are paramount.
How to Choose the Right Power Line Polymer Insulator
Selecting the appropriate polymer insulator requires consideration of several factors to ensure optimal performance:
- Voltage Ratings: Ensure the insulator can handle the specific voltage requirements of your electrical system.
- Environmental Conditions: Assess weather patterns and environmental factors such as pollution levels that may impact insulator performance.
- Mechanical Load Expectations: Determine the anticipated physical stresses on the insulator to select one with appropriate tensile strength.
- Installation Environment: Evaluate the area where the insulator will be installed, considering factors such as accessibility and terrain.