(8318 products available)









































































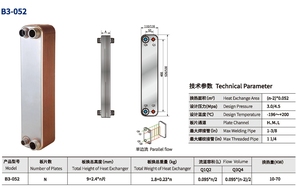
























































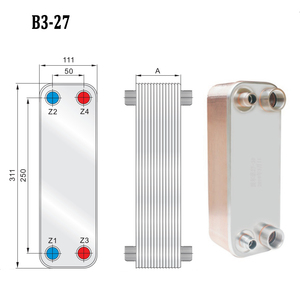









































































There are four main types of plate heat exchangers, including gasketed plate heat exchanger, non-gasketed/premium plate heat exchanger,
fully welded plate heat exchanger
s an d>combined plate heat exchanger. Gasketed plate heat exchangers (PHEs) are gasketed plate heat exchangers used for transferring heat from one fluid to another. Gasketed PHEs are usually used for indoor applications where the exchange of heat is critical. For instance, they can be used for re-heating boilers, cooling of liquids, or even for heating water. Non-gasketed or premium plate heat exchangers have plates that are fully welded on the outside rather than just held together with gaskets. Non-gasketed PHEs are used in high-pressure and temperature applications. They are also ideal for corrosive environments where fluids must be contained fully. Non-gasketed PHEs usually have narrower channels compared to regular PHEs, which helps for greater turbulence and improved heat transfer.
Fully welded plate heat exchangers are cost-effective alternatives to shell-and-tube heat exchangers. They are compact units designed with welded plates instead of gaskets. This construction aids in increasing durability in a range of applications when working under high temperature and pressure. Fully welded plate heat exchangers also save space and hence are a great choice when it comes to having a compact piece of machinery. These types of heat exchangers are used often in oil and petrochemical industries because they can efficiently withstand harsh environmental conditions. Finally, combined plate heat exchanger is also known as the spiral plate heat exchanger. Combined heat exchangers are more flexible as they can be used for heating, cooling, evaporating, and condensing of industrial fluids. They have a special design that helps to increase the velocity of fluids, thus increasing productivity.
MVR plate heat exchangers have the following specifications.
Models
The PHEs modeling plate is distinguished by characteristics such as the quantity, contour, bore, and distance apart of the plates. Various model combinations will produce different heat transfer capacities. Because of their suitability for a wide variety of industrial applications, HBA has several different models in stock.
Size
The plate's size will influence how much heat-mass exchange it can provide. Larger plates entail giant exchangers, but the ratios between the plate lengths, widths, and thicknesses remain constant to ensure performance efficiency. The exact options of sizes of the plates HBA offers are given in the catalog.
Capacity
Heat transfer capacity is dependent on the more prominent capacity of hot fluid exchange and how much cold fluid can go through the exchanger. The more prominent capacities of both fluids may be limited by pressure drop demands in the system. HBA has the formulae and calculations to determine how much capacity is available by the specific pressure drop of the fluids.
The proper maintenance of a plate heat exchanger not only ensures the longevity of the equipment but also optimizes its performance and efficiency. Regular maintenance not only prevents untimely breakdowns but also extends the lifespan of the heat exchanger. By maintaining the appropriateness of each application, businesses can avoid the expense of early replacement or repair.
Frequent inspection is essential. Check whether there is a liquid accumulation, cracking or drooping of gaskets, deformation, leakage occurrence, loosening of bolt connections, or other abnormalities. Do cleaning and sterilization. Mesa plate heat exchangers have the advantage of being easily disassembled. Once opened up, they can be scrubbed clean, ensuring that any leaking fluids do not mix and that hygienic conditions are maintained.
It also pays to be aware of the critical components. The bolts connecting the plates should be firmly fastened, and the gaskets should be checked for any signs of distortion or wear that can lead to leaks between the plates. Corrosion is a common problem of metal parts, so the plate exchanger should be checked for corrosion damage, especially in moist environments or those exposed to chemicals.
HBA is well aware that the costs of proper maintenance will be far less than the intensely costly sudden failure and repair needs. Keeping schedule records of inspections and the observations made will serve as a guiding reference when critical maintenance is needed round the corner.
The main industrial application of a heat exchanger is to cool or heat fluids and separate mixtures. These fluids can be gases or liquids. In the food processing industry, heat exchangers are primarily used for pasteurization, sterilization, and refrigeration. Other plate heat exchanger types applications in the food processing industry include:
Other industrial applications of plate heat exchanger types include:
When selecting a plate heat exchanger for a specific application, it is important to consider each of these parameters to ensure an optimal match between the heat exchanger and the operation needs.
Q1: Why are plate heat exchangers important?
A1: Plate heat exchangers are crucial for several reasons. They boost energy efficiency by recycling waste heat within an industrial process. Using PHE can lower heating expenses, resulting in cost savings. They reduce environmental impact by minimizing energy loss and lowering greenhouse gas emissions. Plate heat exchangers conserve natural resources by reducing energy consumption. They facilitate compliance with regulatory standards that mandate efficient energy use and heat recovery.
Q2: What are the two main types of plate heat exchangers?
A2: The two dominant types of plate heat exchangers are the gasketed and weld bonded. The gasketed plate heat exchanger has flexible gaskets that securely seal and hold the plates together, allowing the fluid to flow through the gaps. It is easily separable for routine cleaning and maintenance. Conversely, the weld-bonded plate heat exchanger has the plates welded together. This permanent fixation makes it rugged and suitable for high-pressure applications. It does not allow disassembly like the gasketed variant.
Q3: What is the life expectancy of a plate heat exchanger?
A3: With proper care and routine maintenance, plate heat exchanger types can last up to 20 years or more.