(603 products available)















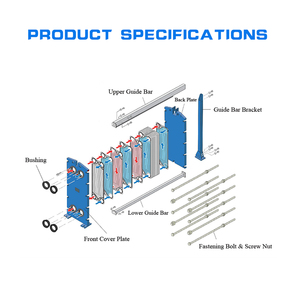













































































































































































































The main types of plate heat exchangers include:
Some specifications of the GEA plate heat exchanger are as follows:
For GEA plate exchangers and any other brands, regular maintenance can extend the machine's life significantly and keep it in tip-top condition.
The plate heat exchangers are widely used in different industries. Some of their most popular applications include.
Food and beverage
Plate heat exchangers are commonly used in the food and beverage processing industry for tasks like pasteurization, sterilization, refrigeration, and cooling drinks and food products. They efficiently transfer heat while maintaining strict hygiene standards, which is really important in the food industry.
Energy and power
In the energy and power industry, plate heat exchangers are widely used in power plants and oil refineries. They are used for preheating feeds, recovering waste heat, and cooling lubricants and gases. Their ability to recover waste heat in power plants contributes to higher efficiency and lower energy consumption.
Marine
In marine applications, plate heat exchangers are commonly used in ship engines for tasks like cooling lubricants, seawater, and engine exhaust gases. Additionally, they find use in onboard refrigeration and air conditioning systems. Their compact size and effectiveness in heat transfer make them ideal for space-saving cooling solutions in marine environments.
HVAC
In HVAC applications, plate heat exchangers are widely used in air conditioning and refrigeration systems, as well as in heating systems. They efficiently exchange heat between refrigerants, water, and air, allowing for effective cooling, heating, and energy recovery in residential, commercial, and industrial buildings.
Chemical
Plate heat exchangers execute various tasks, such as heating, cooling, condensing, and evaporating fluids in chemical processing. They are used in chemical reactors, refineries, and petrochemical plants. The heat exchangers improve energy efficiency in chemical processing and prevent contamination by letting heat transfer occur through a plate.
Powder coat heat exchanger
A powder coat heat exchanger is typically made of stainless steel. It is coated with a powder coating insulating layer. The powder coat plate heat exchanger withstands harsh environmental conditions and resists corrosion and scaling. The heat exchanger is effective in many applications like chemical processing, food processing, mining, and marine industries.
Data center
In data centers, plate heat exchangers are used for transferring heat from server racks to cooling fluids. They help separate the hot servers from the cooling system while allowing heat to be transferred. This is really important for keeping data center equipment working well and avoiding overheating. It allows the system to work better and keeps energy use lower.
Desalination
In desalination processes, plate heat exchangers are used in multi-effect distillation (MED) and multi-stage flash (MSF) desalination plants. They transfer heat from steam to seawater, facilitating the evaporation of water and the production of fresh water. This is really important in coastal areas where access to drinking water is limited.
Application requirements analysis:
Determine the business's specific application needs, including the type of fluid to be heat exchanged, temperature and pressure requirements, flow rates, and the desired heat transfer efficiency. This initial analysis will help set the criteria for selecting a suitable plate heat exchanger.
Size and capacity calculation:
Conduct calculations to determine the appropriate size and capacity of the plate heat exchanger based on the expected heat transfer duty and flow rates. Consider factors such as the available installation space and the potential for future expansion if additional heat exchange capacity may be required later.
Plate design and materials:
Choose the plate design (e.g., chevron, corrugated) that matches the specific heat exchange requirements. Select the plate materials (stainless steel, titanium, etc.) that are compatible with the fluids' chemical properties and mitigate corrosion risks.
Frame and configurable characteristics:
Decide on the heat exchanger's framework materials and structure based on strength, durability, and maintenance needs. If configurability is essential, ensure the heat exchanger can be easily reconfigured to adapt to changing process requirements.
Maintenance and cleaning:
Consider the maintenance and cleaning requirements of the selected plate heat exchanger. Look for designs that facilitate easy access for cleaning and maintenance, minimizing downtime and operational costs.
Compliance and certification:
Ensure that the selected plate heat exchanger complies with relevant industry standards and regulations for the specific application. Check for the necessary certifications to meet quality and safety requirements.
Cost and budget analysis:
Evaluate the initial investment cost of purchasing the plate heat exchanger and consider the long-term operational and maintenance costs. Perform a cost-benefit analysis to select a heat exchanger that aligns with the business budget and provides a favorable return on investment.
Q1 What are the differences between the working principle and features of GEA plate heat exchangers and tube heat exchangers?
A1 Plate heat exchangers are constructed by many thin metal plates assembled between two frames. They exchange heat by the fluids flowing in opposite directions. As for tube heat exchangers, they consist of a bundle of tubes, where one fluid flows through the inner part of the tube, while the other flows outside. The two heat exchangers have different compactness. Plate heat exchangers occupy smaller spaces than tube heat exchangers. Furthermore, they are more efficient because of their larger surface area. GEA plate heat exchangers also have high efficiency thanks to the corrugated design of the plates.
Q2 What are the benefits of GEA heat exchanger cleaning?
A2 Regular cleaning removes the deposits sticking to the equipment and improves the heat transfer efficiency. Maintaining the equipment's capacity limits the energy expenses. Furthermore, it prolongs the service life of the heat exchanger.
Q3 What factors determine the prices of heat exchangers?
A3 The main factors are the materials, dimensions, structure, and connecting ways. Generally, plate heat exchangers are more compact than tube ones, making them more affordable. In comparison, shell-and-tube heat exchangers are typically more expensive, as they require more materials and complex manufacturing processes.
Q4 What is the lifespan of a heat exchanger?
A4 On some conditions like the material compatibility, the fluids' corrosiveness and temperatures, the pressure, the flow rates, and the installation, the lifespan can vary between 5 and 30 years.