(303 products available)























































 Ready to Ship
Ready to Ship
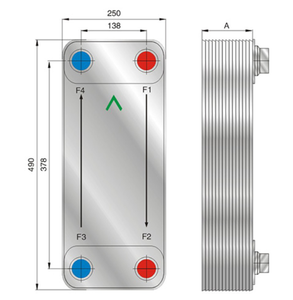






























































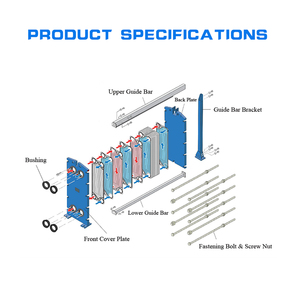
















































































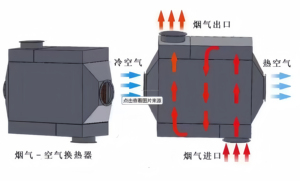


















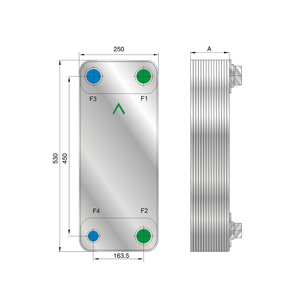
Plate heat exchangers are widely used apparatuses for transferring heat from one fluid to another fluid without mixing them. The fluids can be gas, liquid, or a combination of both. Heat transfer is accomplished by the means of metal plates with high thermal conductivity that separate the two fluids. According to the structure and material, plate heat exchangers can be divided into several kinds.
Wide gap plate heat exchanger
This kind of heat exchanger has wide gaps between the plates. It is suitable for fluids with particles to prevent plugging. It is usually used in the food industry. Sometimes, the fluids have to be sterilized in the process. So, they have to be heat exchangers that can withstand sterilization. Heat exchangers that can withstand sterilization are also known as sanitary wide gap plate heat exchangers.
Falling film plate heat exchanger
It is designed for falling film cooling or heating processes. It utilizes falling films to enhance heat transfer efficiency. Falling film plate heat exchangers are characterized by compact structures, rapid heat transfer rates, and energy-saving performance. They are widely used in industries such as petrochemicals, food processing, and power generation.
Nanofluid heat exchanger
Nanofluid is a new type of fluid used to transport heat, which improves the thermal conductivity of the fluid. Nanofluid plate heat exchangers use nanofluids as the working medium to enhance heat transfer. Their advantages include higher heat transfer rates, reduced pressure drops, and smaller equipment sizes. Nanofluid plate heat exchangers have broad application prospects in energy, chemicals, and other high-demand industries.
Double-pipe heat exchanger
A double-pipe heat exchanger consists of a pair of pipes, one of which is placed inside the other. The inner pipe carries the hot fluid, and the outer pipe carries the cold fluid. Double-pipe heat exchangers are simple, compact, and easy to manufacture. They are suitable for small-scale heat exchange applications and low- to medium-sized production.
Gasketed plate heat exchanger
The gasketed plate heat exchanger divides fluids by gaskets. The gaskets seal the fluids on each side of the plates and direct the two streams across the plates of the heat exchanger, which conducts heat between the two fluids. Gasketed plate heat exchangers are flexible, efficient, and easy to maintain. They are widely used in HVAC, refrigeration, and other industrial fields.
Freon Plate Heat Exchanger Specs
The specifications of a plate heat exchanger Freon can vary based on different models and manufacturers.
Here are some key specifications to take note of:
- Heat Transfer Area: This is the size of the effective working area of the plate heat exchanger. It is usually made up of several plates. The Heat transfer area can be small or large depending on the specific use and demand of the device.
- Flow Rate: The amount of fluid or gas that passes through the heat exchanger plates per unit time. It is usually stated in units like cubic meter per hour (m3/h) or liter per minute (L/min).
- Temperature Range: The Freon plate heat exchanger works within a defined temperature range. The temperature of the incoming fluid or gas must not exceed this range. Some heat exchangers also have a specific maximum allowable temperature.
Maintenance
Plate heat exchanger Freon requires regular maintenance and inspection to ensure that it works well and to prolong its service life. Some maintenance tips are as follows:
- Regular Cleaning: Heat plates will inevitably get contaminants over time, like dust or debris. So, it is important for users to regularly clean the plates on both sides of the heat exchanger. The initial step to cleaning is to disconnect the power supply and then take apart the heat exchanger. Next, with clean water or a suitable cleansing agent, users should wash the surfaces of the plates carefully to ensure that there are no contaminants left. Also, make sure that the plates are completely dried before users assemble them again.
- Inspect For Leaks: Users should often check if the plate heat exchanger is leaking. They should inspect the components carefully and if they see any traces of liquid leakage, they should find and fix the cause of the leakage immediately. Be sure to check things like the sealing gaskets, bolts, and nuts.
- Replace Gaskets: Over time, the sealing gaskets in the plate heat exchangers may wear out or become damaged. Hence, users should regularly inspect these sealing gaskets and replace them promptly if they find any cracks or deformation in the gaskets.
- Pay Attention to Airflow: It is important to note that an appropriate airflow is critical to the operation of a plate heat exchanger set. During maintenance, users should ensure that there aren't any objects blocking the inlet or outlet of the exchanger.
Applications of plate heat exchanger Freon include the following industries.
Food and drink processing
Pasteurized milk, liquid egg, juice, and ice cream are some Freon plates heat exchangers used in food and drink processing. For milk, an inbound temp of 4°C is heated to 85°C for cooling and pasteurization. Then, the outbound milk that has cooled to 10°C is sent for processing. Freon heat exchangers are also used to heat water and other liquids in food facilities prior to cleaning and sterilization.
Power generation
Freon plate heat exchangers are used in power generation through the indirect cooling of gas or steam. The large exchangers can even recover waste heat to improve the efficiency of current power systems. Waste heat recovery can also reduce greenhouse emissions by cooling the gas.
HVAC
In residential or commercial heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems, Freon plate heat exchangers play the crucial role of transferring heat from refrigerant coils to air or water. The task can involve condensers, evaporators, coolant coils, and cooling towers. Freon exchangers are as effective as tube exchangers but occupy less space. Freon exchangers also have less cost and require less energy to operate.
Chemical processing
Plate heat exchangers are ideal for chemical processing factories that use viscous fluids as input. In such facilities, Freon exchangers will be the preferred models. The reason is plate exchangers are easier to clean than traditional tube models. Cleaning is necessary since the fluids may contain fats or chemicals that can stick to the surfaces.
Marine industry
Freon plate heat exchangers are used in ships and marine vessels for engine cooling, cabin heating, and freshwater generation. The strong construction of Freon exchangers makes it possible for them to work in sea water. An added benefit is that they are compact and lighter in weight than tube exchangers.
Oil and gas
In the oil and gas industry, Freon plate heat exchangers perform crude oil preheating, cooling, and heat recovery tasks. As features of Freon exchanger machines, buffered plates and inspected securing bolts help operators easily keep the machines working and securely fastened in one place.
Solar plants
Solar panel plates heat exchangers cools panels in solar plants. Freon heat exchangers transfer heat from the solar collector to the working fluid. Freon exchangers transfer heat from working fluid to boiler or steam generator.
Pharmaceuticals
The basis of Freon plate heat exchangers' use in pharmaceutical industries is their need for hygiene and cleanliness. The exchangers are used to heat or cool bio-reactors, fermenters, process tanks, and more.
Consider the surface area:
The surface area should be sufficient for the required heat transfer. Even if a compact plate heat exchanger is available, it is typically designed to provide up to 45% more surface area than shell and tube heat exchangers. So, make sure to check if the surface area is sufficient.
Check temperature and pressure ratings:
Ensure the heat exchanger can handle the Freon's operating temperature and pressure. Look for heat exchangers specifically rated for Freon applications.
Look for corrosion-resistant materials:
A plate heat exchanger's materials can significantly impact its lifespan. Consider high-quality stainless steel plates (such as 316) or epoxy-coated plates for added protection. Epoxy-coated plates have a thin layer of epoxy on the surface, making them more resistant to Freon's potential corrosiveness.
Evaluate the design:
Focus on plate heat exchangers with efficient designs, such as chevron-patterned plates. These designs enhance turbulence and improve heat transfer co-efficients.
Consider the size and weight:
If space constraints or weight limitations exist in the refrigeration system, compact and lightweight plate heat exchangers would be ideal.
Assess serviceability:
Consider the serviceability of the heat exchanger. It means checking whether it has removable end covers and access points for cleaning, inspection, and maintenance. Also, assess the availability of service centers and technical support for the specific brand and model chosen.
Q1: What is the purpose of a plate heat exchanger in refrigeration and cooling applications?
A1: The purpose of a plate heat exchanger in refrigeration and cooling applications is to transfer heat between different fluids while keeping them separated. This allows for cooling, heating, or temperature regulation of the fluid being processed in refrigerators and coolant systems.
Q2: Why are plate heat exchangers preferred over other types of heat exchangers in industrial applications?
A2: Plate heat exchangers are preferred over other types of heat exchangers in industrial applications because they occupy less space and have the advantage of easy cleaning and maintenance. Furthermore, plate heat exchangers are efficient, versatile, and cost-effective.
Q3: Do plate heat exchangers need to be insulated?
A3: Yes, plate heat exchanger insulation is suggested. Insulating a heat exchanger can help to minimize energy loss owing to heat transfer to the environment, increasing the system's overall efficiency.
Q4: Do plate heat exchangers have a future market?
A4: The market for plate heat exchangers is expected to grow in the near future because of the increasing demand for efficient heat transfer solutions in numerous industries.