(132 products available)




























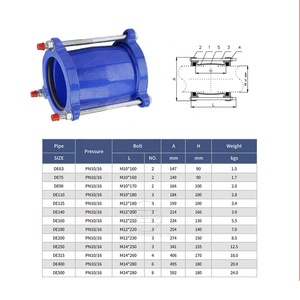





















































































































































Suppliers provide these types of gibault joint coupling to buyers in bulk.
These couplings compensate for shaft misalignment. They dampen vibrations and absorb shocks. Flexible couplings cater to applications in motors and pumps. They ensure smooth power transmission despite mechanical stresses.
In rigid couplings, alignment precision is non-negotiable. These are suitable for steady torque transmission in consistently aligned shafts. Industries that deal with precision in rolling mills or conveyors prefer stiff couplings. Rigid couplings provide robust support without flexibility.
Spacer couplings are functional where intermediate shaft sections require installation or removal ease. Industries with periodic maintenance demands, like chemical processing plants, use spacer couplings. They incorporate these couplings to ensure easy access without disrupting operations.
Oversized couplings support larger shafts in demanding applications. These dense couplings are useful in heavy industries like mining and steel production. They handle elevated torque and sustain durable equipment. The correctly sized oversized coupling prevents shaft damage while maintaining energy efficient transmission.
Purchasing managers should consider these applications for silent chain couplings.
People widely use the gibault joint in water and wastewater applications. It connects pipeline sections with utmost reliability. The joint's resilience against corrosive elements makes it ideal for water treatment facilities. These attributes ensure operational longevity and maintenance cost reduction.
The oil and gas industry favors gibault joints. Pipeline infrastructure in this sector requires secure and leak-proof connections. As a go-to for transferring liquids and gases, these joints withstand harsh environmental conditions.
People in mining rely on gibault joints for slurry and chemical pipelines. They ensure smooth and efficient material transport. Durability and resistance to abrasives make gibault joints indispensable for mining operations.
Power plants require reliable pipeline connections for steam, water, and other fluids. The gibault joint's ability to handle high pressure and temperature makes it a vital component in power generation systems. It supports the efficient operation of thermoelectric and hydropower plants.
In manufacturing, people use general purpose coupling in pipelines for diverse fluids and chemicals. They connect metal pipes while resisting corrosion. This resistance is crucial for the transportation of caustic chemicals. Consequently, they are a staple in chemical plants.
This section contains some specifications and features buyers should consider for universal joint couplings.
Chambers
A gibault joint has dual halves, each fitted with grooves designed to receive and hold rubber o-rings. It also has a middle section that features a tapered end on both sides, creating a valley-like dip that facilitates the rubber o-ring's compression upon joint coupling.
Rubber O-rings
The rubber o-rings slide into the grooved chambers of the two halves of the gibault joints. They act as shock absorbers, providing the needed flexibility for slight misalignments between pipe sections.
Coupling Pin
An installation of a metal tapering coupling pin runs through the joint's center. This pin secures the two joint halves together. It anchors them firmly to prevent disconnection, even under intense pressure conditions.
Sleeve
In a gibault joint, the coupling pin is housed securely within a cylindrical metal sleeve that encases the pin's tapered ends. This design ensures easy installation and removal of the pin when necessary.
Materials
Manufacturers construct the Gibault Joint mainly from high-strength steel alloy. Some options may include stainless steel. This durable materials offer superior resistance to corrosion, wear, and fatigue in tough environments.
To install, follow these steps:
The joint's pipe ends must be cleaned and prepared to ensure a smooth and secure connection.
The coupling pin and sleeve are removed after securing their corresponding pipe sections.
People insert the pin into the tapered ends of the two adjacent pipes.
A person secures the pin by reinserting the sleeve. They lock the pin in place to create a tight bond.
The setup is finally tested for leaks and proper alignment to ensure operational integrity.
Regular Inspections
Frequent checks for signs of wear, corrosion, or damage are necessary. They should do this on both the rubber rings and the joint's metal components.
Lubrication
Proper lubrication people do it routinely to minimize friction and guarantee the joint operates smoothly. This action also lengthens the life of the gibault joint.
Ring Replacement
With constant use, the joint's rubber o-rings will wear out. People replace them regularly to maintain the coupling's integrity and strength.
Monitor Pressure Levels
Avoid exceeding the recommended pressure limits of the gibault joint. Intensive pressure can damage the coupling and compromise its functionality.
Look at these quality and safety factors for chain couplingsembark on.
Manufacturers make gibault joints from premium-quality steel or alloy. This material choice ensures the joint endures extreme pressures and a variety of temperatures. Hence, users should prioritize joints with certified materials that meet industry standards. For example, ASTM or ISO specifications.
People routinely inspect gibault joints to locate any signs of wear or corrosion. Signs of wear or internal damage can lead to joint failure. Inspections here should happen before installation and periodically throughout their use. Advanced non-destructive testing methods like ultrasonic inspections are also effective.
Every gibault joint comes with specific load and pressure ratings. These ratings help determine the suitable applications for which the joint is intended. User should never exceed these ratings. Going over them can cause catastrophic failures or even joint separation.
The joint's rubber o-rings have to function properly for a long time. People replace them as needed and ensure sealing integrity remains uncompromised. Check for cracks, hardening, or any signs of chemical degradation on the o-rings. Compromised seals allow leakages of fluids or gases.
Operating or maintaining gibault joints requires in-depth knowledge of their working principles. Therefore, users should give their employees sufficient training. Employees with this training will be more equipped to recognize potential problems. Consequently, this recognition will minimize safety risks.
Yes, people can use these joints in cryogenic applications. Manufacturers make them from materials that withstand extremely low temperatures. Therefore, they perform well in liquefied gas transport systems.
The primary benefit of using joint coupling in pipeline systems is its ability to provide flexible connections. These flexible connections accommodate thermal expansion and contraction. As a result, it reduces stress on the pipes.
Although they have a long life, routine maintenance like inspections and seal replacements will keep them in prime condition. In high-demand situations, maintenance often needs to be more frequent to be effective.
Those who prefer not to use gibault joints typically opt for welding or mechanical fittings instead. Both options can provide versatile sealed connections for metal pipelines. However, they each lack the flexibility that gibault joints offer.
The rubbber seals people call them act as vibration dampers. The seals ease the stress of one metal pipe on another connected pipe.