(2807 products available)
















































































































































































































F8 filter bags are produced using different types of synthetic fibers. Here are some of them:
Nylon
Nylon filter bags are both strong and resilient. This allows them to be used in filter bag applications requiring high pressure. They have high elasticity, tensile strength, and resistance to abrasion. Nylon filter bags can efficiently collect fine powders for which it is difficult to achieve an average filter bag efficiency. They are also resistant to mildew. Nevertheless, the nylon filter bag is not strong against heat and acids.
PES
(Polyester)
This type of filter bag is made of woven or non-woven polyester fabric. These bags have excellent resistance to heat, making them ideal for high-temperature filtering processes. Additionally, the structure provides a high level of filtration efficiency, ensuring that even the finest particles are captured effectively.
PES / PERT
_ (Polyester / Polytetrafluorethylene) _
PES / PERT filter bags combine the properties of polyester and PTFE (Polytetrafluorethylene), a substance that is both strong and resistant to high heat, increasing the filter bag's performance and durability, while also enhancing the efficiency with which microparticles are captured.
Compound fiber
_ filter bags _
These filter bags are made from a combination of synthetic fibers, which results in high durability, filtration efficiency, and resistance to heat and static electricity.
Antistatic filter bags
_ filter bags _
These filter bags are made with anti-static fibers, which help to prevent dust from accumulating on the surfaces of the bags. This leads to an extended lifespan for both the bags and the filters.
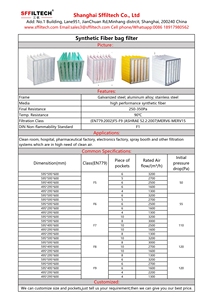
Sizes and dimensions
The length and diameter determine the fit in the filter housing. Standard ones like 3' x 5', 4' x 6', or 6' x 8' often work with most filters. Custom sizes can be made to order for unique systems.
Top and bottom components
The upper part of the filter bag, called the "top", secures it in place while filtering. Common types of tops are snap bands, steel rings, and flanges, each providing different levels of hold. The "bottom" is usually a collar or clamp that gently siphons liquids from the bag without damaging them.
Seal methods
Filter bags must be sealed tightly; otherwise, contaminants can enter the process. Heat sealing, RF (radio frequency) sealing, or sewn seams can be used. Heat sealing creates a robust, leak-proof seam that resists tearing from filter cake buildup. Sewn seams provide more flexibility but must be carefully stitched to prevent leaks. Choosing the right sealing method is crucial for effective contaminant control.
It is essential to ensure proper maintenance and care of the F8 filter bags to extend their lifespan and maintain filtration efficiency. Here are some tips to keep them in optimal condition:
Industrial filter bags have a wide range of applications across different industries.
When buying industrial air filter bags for machines, one must consider various features related to the bag's design and filtration. One must be cautious because these bags play a critical role in equipment and air filtration. To start with, people buy the filter that fits the buyer's machine, such as the F8 bag, by checking the frame, height, width, and depth of the filter. It's vital to ensure that the filter has the proper sealing mechanism and fits the machine properly to avoid any leaks.
The type of media chosen will depend on the particles people are filtering. For fine particles like dust and pollen, a synthetic media filter bag would work well. However, for more specific industries and types of particles, a more specific media may be required, like activated carbon for gas and odors or a melt-blown polypropylene for microscopic particles.
F8 filter bags come in different shapes and sizes to fit different collecting hoppers and combustion processes. Usually, the more commonly used types are round, flat, pleated, and square. The fineness of the filtration chosen will also depend on the type of filter bag being used and the type of furnace or pulverizer the filter is being used for. F8 is a fine-dust filter, while other bags may only filter larger particles.
Another consideration when buying filter bags is what coating one should use that will resist which chemicals in the industrial environment one needs to work in. Coatings can add to the filter bag's life and improve the filter bag's resistance to certain chemical reactions and high temperatures.
One can get industry-specific filter bags when searching for some in the industrial filter-bag-searching market. For example, food processing would require a different kind of filter bag than, say, an iron ore filter bag. In the food industry, one may need a filter bag with biofiber, while in the cement industry, one would need a filter bag with fiberglass.
It is essential to research the reputation of the suppliers of filter bags because the quality of the filter affects the whole air-extraction system. A poor-quality filter bag will result in more bags being needed because of their short life, thus, increasing costs in the long run.
Q1: What is an air filter bag made of?
A1: An air filter bag is commonly made of synthetic, glass, cotton, wool, or polyester fiber. High-temperature or chemical-resistant fiber, like aramid, needs to be used for industrial filter bags.
Q2: Why are air filter bags tubular?
A2: Tubular or sock-shaped filter bags allow free movement inside the filter housing. This movement aids dust release from the bag during bag cleaning.
Q3: What does the F in filter bag classes denote?
A3: The letters after the number categorize the filter efficiency. The F filters are finer than the E filters, with the F8 bags among the finest.
Q4: What are some other types of air filters?
A4: Some other types include electrostatic air filters that use electricity to trap particles, HEPA filters that meet strict criteria to capture at least 99.97% of relevant particles, and UV filters that kill bacteria and viruses.