(256 products available)































































































































































































































An EPP foam making machine manufactures expanded polypropylene (EPP) foam, a plastic material widely used in automotive, packaging, and toy industries due to its lightweight, durability, and energy-absorbing properties. The process of making EPP foam involves creating expandable polypropylene beads, which are then expanded and fused together using heat and pressure to form a foamy block or sheet.
Two main types of machines are commonly used to produce EPP foam: bead production machines and foaming machines.
Bep production machines:
An EPP foam machine will make small beads of polypropylene, also known as pre-foamed beads. The process may involve the use of a pre-foamer, an expansion machine, and an air compressor. The air compressor supplies the necessary pressure to expand the beads, while the pre-foamer ensures that the beads are adequately prepared for the expansion process. Once the steam is introduced by the expansion machine, the air pressure causes the beads to expand, forming tiny, lightweight particles that make up the EPP foam.
Foaming machines:
Once the beads are prepared, an EPP foam forming machine will be used to shape and fuse them into EPP foam products. This may involve the use of an oven, a mold, and a hydraulic or pneumatic system. The beads are placed in a mold, where heat is applied (often through the use of an oven). The heat causes the beads to expand further and fuse together, creating a solid mass of EPP foam. The foaming machine may use a hydraulic or pneumatic system to control the opening and closing of the mold, as well as the pressure applied to the beads inside the mold.
Foaming machines can be further divided into two categories based on the type of heating element used to expand the beads:
Steam heating molds:
In these machines, the molds are heated with steam to expand and fuse the beads. The steam provides the necessary heat for the beads to expand and stick together, forming a cohesive foam structure. Molds with an EPP foam heating plate are another variation of this machine. In this case, the plates are heated electrically, providing a more uniform and controlled heating process.
Conductive heating molds:
In some foaming machines, conductive heating is used. This involves the use of heated plates or other conductive materials that transfer heat to the EPP beads, causing them to expand and fuse together. Conductive heating allows for even heating throughout the mold, ensuring consistent foam production.
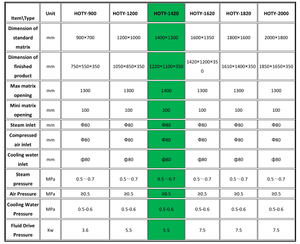
Production capacity:
The capacity of an EPP foam manufacturing equipment indicates the amount of EPP foam it can produce in a given time. This is typically expressed in units per hour or per day. For example, a piece of equipment with a production capacity of 500kg/h means it can produce 500kg of EPP material per hour.
Raw materials:
EPP foam making equipment requires specific types of raw materials to produce EPP foam. The two main raw materials are propylene and foaming agents. The quality and compatibility of the raw materials are crucial to the normal operation and final product quality of the equipment.
Machine size:
The machine dimensions of EPP foam manufacturing equipment usually include length, width, and height. These dimensions determine the space occupied by the equipment and its installation requirements in the production site. The machine size needs to match the available space on the production floor to ensure proper installation and use.
Power requirements:
Power requirements refer to the power needed by EPP foam manufacturing equipment for its normal operation. This is usually expressed in kilowatts (kW) or horsepower (HP). Power requirements determine the power supply and electrical facilities needed to support the equipment's operation in the production environment.
Operating temperature and pressure:
EPP foam making machines usually operate at specific temperature and pressure ranges to ensure the foaming and molding processes of the raw materials. These temperature and pressure ranges are critical for controlling the quality and properties of the final EPP foam products.
Automation and control system:
The automation and control system of EPP foam production equipment enables automatic control and monitoring of the production process. This includes the computer system and software used to manage production, as well as the automated devices and sensors for measuring and monitoring. The automation and control system enhances the precision and efficiency of production, as well as facilitating the equipment's operation and maintenance.
Maintaining and caring for the EPP foam making machine properly can ensure its good performance, prolong its service life, and improve production efficiency. Here's some maintenance and care advice:
Regular cleaning:
Regularly clean the entire machine, including the mold, feeding system, cooling system, etc. Use appropriate cleaning agents and tools to avoid damaging the surfaces and precision of the equipment. Also, pay attention to the removal of dust and residues in the equipment.
Lubrication system maintenance:
The maintenance of the lubrication system of the EPP foam-making machine is critical to its normal operation and prolonged service life. Regularly clean and replace the lubricating oil to ensure that the lubricating oil is free from impurities and ensures good lubricating performance. Check the lubrication points and make sure the lubricating oil is applied to the proper locations as required. Additionally, users should monitor the operating temperature of the lubricating oil pump. If the temperature is too high, cooling measures should be taken in time to avoid damage to the equipment due to overheating.
Regular inspection and maintenance of key components:
Users should regularly inspect and clean the key parts of the EPP foam-making machine, such as the heating element, cooling system, etc. This will ensure that they are in good working condition. Additionally, they should promptly replace worn or damaged parts to ensure stable equipment operation and prevent quality issues in production.
EPP foam making machines are widely used in packaging, toys, building materials, automotive, and other industries.
When choosing an EPP foam machine, the primary focus should be on the production requirements. These include the desired end products and their specifications, such as product size, shape, and density. Additionally, the quantity of items that the buyer intends to produce also plays a significant role. This is because potential manufacturing speed and capacity of the machine are necessary to meet the required output.
The available floor space and layout also have a part in determining the suitability of a machine. As machines come in different sizes, what an operator has at the manufacturing facility may determine the choice of equipment. Also, consider the technical skills of the existing workforce. Some machines require specialized technical knowledge, so buyers must get equipment that their workers can handle with ease.
Since the machine will be part of the production line, assess the ease of integration it provides to other existing production equipment. Set up costs may go up if it cannot connect to the other tools efficiently. Cost is an important factor in deciding on the appropriate EPP machine. Aside from the upfront purchase price, buyer should factor in energy requirements, maintenance expenses, and spare part costs.
Finally, the long-term considerations that come with the machine should be evaluated. Consider its potential resale value when the business is looking to sell off some equipment to reinvest in other parts of the business. With proper maintenance and care, some machines can retain their value and fetch a good price in the resale market. Also, take into account the energy efficiency of the machine. An EPP machine that uses less energy will keep production costs low and significantly foam cutting machine contribute to the company's bottom line.
Q1: What type of materials can the EPP foam machine process?
A1: The EPP foam machine can handle various types of polystyrene, including expanded polystyrene (EPS), extruded polystyrene (XPS), and solid PS.
Q2: Can users integrate automation into their EPP foam machines?
A2: Yes, it's possible to automate some processes and integrate different types of automated systems for more efficient production.
Q3: What are the maintenance requirements for EPP foam machines?
A3: Regular inspection and cleaning of vital parts, lubrication of moving components, calibration and tracking of automatable systems, and periodic professional servicing are all critical to the EPP machine's longevity and performance.
Q4: Are there any specific safety regulations to consider when using EPP foam machines?
A4: Yes, safety rules are determined by the country of use. Operators must follow general safety standards, including those relating to electrical and mechanical equipment. They must also take particular precautions concerning the materials processed by EPP machines and any potentially hazardous emissions.