(1942 products available)








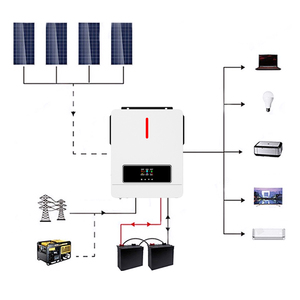








































































































































































































Solar inverters, primarily known for converting direct current (DC) into alternating current (AC) to allow residential and business applications to effectively use available solar energy, come in various types.
Although 8 KVA solar inverters also feature additional functionalities, such as energy storage management and smart technology integration, which help promote energy efficiency, the following are the main types of solar inverters available:
8kva string solar inverters are the most simplistic and popular in the commercial and residential solar installation space. The advent of string inverters especially arose due to the widespread installation of residential rooftop solar systems.
These inverters connect to a series of solar panels, which form a string. This setup enables the panels to generate energy and, at the same time, allows the inverter to convert the DC power into AC power for use.
However, in case one solar panel in that string malfunctions, it will affect the other panels' production capacity, leading to possible energy losses. Nevertheless, an 8kva solar inverter is still ideal for medium-sized properties, and its easy installation is one of its greatest advantages.
A hybrid solar inverter is a type that combines features of string/grid-tie and off-grid inverters. They are used with solar batteries and work well in systems that need storage capabilities to provide energy during blackouts or at nighttime.
These inverters allow real-time energy storage management and storage for later consumption. This unique ability helps make hybrid inverters the ideal energy management solution for those who want to increase their energy resilience. A hybrid 8kva solar inverter, while more complex and possibly expensive than string and regular inverters, offers functionality valued highly in an energy crisis.
Microinverters differ significantly from string inverters in that they are not centralized in the system but rather localized. Each solar panel has a mini-inverter attached to it, one that converts the DC power generated by the panel into AC power independently.
This distinctive feature makes microinverters especially effective in ideal conditions, as they allow each panel to perform optimally. This quality improves, as ascertained, that when one panel is in the shade, dirty, or even experiencing a malfunction, it will not affect the other panels' production capacity.
Although microinverters are more predisposed to being individually installed, they are extremely effective for roofs that have multiple shading, orientations, or tilts. An 8kva microinverter is perfect for small to medium-sized homes.
Grid-tie solar inverters are inverters that are designed to work with the utility grid, which means they have to operate synchronously with the grid frequency. These inverters feed excess energy generated by the solar system back into the grid where the system is connected.
If the grid goes down, grid-tie inverters are designed to automatically shut down as a safety measure. They are the most commonly used in residential and commercial solar systems. An 8kva grid-tie inverter is particularly appropriate for medium-sized residential and commercial properties.
Off-grid inverters are inverters that are designed to directly power energy loads while charging batteries for energy storage. These inverters are used in solar systems that are not connected to the utility grid. In such cases, the inverters would provide power from the batteries at nighttime or during periods of heavy overcast.
Off-grid inverters are used in remote homes or communities that cannot access power lines. An 8kva off-grid inverter is good for medium-sized homes and small cabins in remote areas.
8KVA solar inverters are very appropriate in industrial settings as a means of boosting energy efficacy, enhancing redundancy, and lowering power costs. Below are some key industrial applications of 8kva solar inverters:
In situations where power shortages can result in dire consequences, 8kva inverters are used to consistently power critical systems.
For example, in data centers, telecommunications networks, and emergency response settings, the uninterrupted power supply with 8kva inverters helps maintain operations and safeguard important equipment.
Industries have highly variable energy demands, which means that at certain times, energy needs are greater than at other times. In such peak periods, the cost of electricity tends to increase significantly. However, using 8kva solar inverters during peak hours allows industries to utilize solar energy and reduce dependence on the grid.
This dependence leads not only to substantial savings in utility bills but also to reducing the strain on electrical infrastructure. In addition, during periods of lower energy demand, 8kva inverters can be employed to heap energy (if compatible batteries are integrated into the system) for evening or early morning use.
A lot of industries are located in areas unaccessible by the utility power grid. In these areas, 8kva solar inverters are essential for powering operations like mining, oil and gas extraction, and agriculture. These inverters work together with battery storage systems to ensure consistent power availability even when sunlight is not present.
Furthermore, modern 8kva inverters include smart technology that can help industries optimize energy usage, monitor performance in real time, and improve energy management.
With the increase in energy regulations, industries are adopting renewable energy solutions to comply with environmental standards.
8kva solar inverters are an integral part of these initiatives, allowing industries to decrease greenhouse gas emissions, minimize their carbon footprint, and contribute to improved air quality.
These are not just regulatory compliance strategies but corporate sustainability initiatives that enhance brand reputation, attract eco-conscious customers and investors, and improve workforce morale.
Industries are also investing in electric vehicle (EV) charging stations for employees and visitors. An 8kva solar inverter can provide sufficient power for multiple charging stations, allowing industries to use solar energy to support their EV charging needs.
This setup is a dual benefit of lowering grid reliance and supporting the transition to more sustainable transportation options. Overall, the flexibility and efficiency of 8kva inverters are crucial for optimizing energy use in various manufacturing processes.
The 8KVA solar inverter is typically compatible with different solar modules and batteries and boasts various technical features that enhance the solar system's operational effectiveness. Here is a rundown of these features:
The selection for an 8KVA inverter will depend on various factors. Here are these key factors when choosing the inverter that applies inwhichever where the solar system is used:
Choosing the suitable solar inverter is essential for the effective operation of the solar system; for medium-sized homes, commercial buildings, and industrial facilities, an 8kva string inverter would work well fine. A hybrid inverter is ideal for those wanting to add batteries to their system for enhanced power reliability.
On the other hand, microinverters, although more costly, should be considered where there is potential panel shading, as they will help overcome this problem.
For properties near electrical substations, grid connection will be easy, and a grid-tie inverter will be used. Such properties that cannot access utility power must use an off-grid inverter while ensuring their system includes sufficient battery storage.
Hybrid inverters use certain battery types, including lead-acid, lithium-ion, and gel batteries, so it is imperative to ensure the battery used is compatible with the hybrid inverter.
The solar inverter is the component in the solar system with the potential to affect the overall system performance negatively if the wrong one is used. This is because, to operate optimally, each solar inverter has a distinct maximum power input. This power input should be equally distributed among the solar panels integrated into the system.
Therefore, if the solar panels used are not the same or compatible with the inverter, there will be performance issues. For instance, an 8kva microinverter and string inverter will require about four solar panels each, meaning that in total, there will be eight panels in the system.
The maximum input power should also be considered; for example, if the inverter model has a max power input of 1000 watts, then the solar panels used should have a combined wattage of not more than 1000 watts. A property owner should also consider other factors like the wattage of the inverter to ensure the inverter can adequately cater to the energy needs.
All inverter types have distinct price ranges. While hybrid inverters are generally more expensive than grid-tie and string inverters, they offer benefits, such as increased energy reliability and storage capacity, that may warrant the additional cost.
Microinverters are more costly than the centrally installed inverters. Although the affordability of the inverter is critical, the maintenance costs over time should also be factored in. That is, the maintenance cost of hybrid and microinverters is higher than that of string inverters.
Professional installation is an essential determinant of the performance of the solar inverter system. String and grid-tie inverters are easier to install than hybrid and microinverters.
Some of the many advantages of this inverter include:
The solar inverter is meant to last between 5 to 10 years. An 8kva solar inverter can last longer with proper maintenance and care.
An 8kva inverter is a device that transforms direct current (DC) into alternating current (AC). In this case, an 8kva generator output voltage will be about 67 volts. This 8kva inverter will generate power for homes and businesses using solar energy by storing current in batteries.
Currently, the average cost of a solar inverter in the marketplace is between 100 to 200 US dollars. This value will depend on various factors, including the solar technology used in providing renewable energy, operational and maintenance costs, location, and prevailing government policies.