(8168 products available)




































![Travel Carbon Monoxide <strong>Detectors</strong> Portable with Alarm [<strong>3</strong>-in-<strong>1</strong>] CO <strong>Detector</strong> | Humidity |Temperature Co <strong>Gas</strong> Monitor](http://s.alicdn.com/@sc04/kf/H9a089aab75e348d6a60abaaa8d019d08o.jpg_300x300.jpg)
![Travel Carbon Monoxide <strong>Detectors</strong> Portable with Alarm [<strong>3</strong>-in-<strong>1</strong>] CO <strong>Detector</strong> | Humidity |Temperature Co <strong>Gas</strong> Monitor](http://s.alicdn.com/@sc04/kf/H00eab3724ee54c6891cdbc4c8b875dd0V.jpg_300x300.jpg)
![Travel Carbon Monoxide <strong>Detectors</strong> Portable with Alarm [<strong>3</strong>-in-<strong>1</strong>] CO <strong>Detector</strong> | Humidity |Temperature Co <strong>Gas</strong> Monitor](http://s.alicdn.com/@sc04/kf/H75dab0716d894fb5bb321e83715a5a9ei.jpg_300x300.jpg)
![Travel Carbon Monoxide <strong>Detectors</strong> Portable with Alarm [<strong>3</strong>-in-<strong>1</strong>] CO <strong>Detector</strong> | Humidity |Temperature Co <strong>Gas</strong> Monitor](http://s.alicdn.com/@sc04/kf/Hdc396b1a982c4c6e8d1818d979cc307cx.jpg_300x300.jpg)
![Travel Carbon Monoxide <strong>Detectors</strong> Portable with Alarm [<strong>3</strong>-in-<strong>1</strong>] CO <strong>Detector</strong> | Humidity |Temperature Co <strong>Gas</strong> Monitor](http://s.alicdn.com/@sc04/kf/H2a56b864322a4fa698825332b99eb73aS.jpg_300x300.jpg)
![Travel Carbon Monoxide <strong>Detectors</strong> Portable with Alarm [<strong>3</strong>-in-<strong>1</strong>] CO <strong>Detector</strong> | Humidity |Temperature Co <strong>Gas</strong> Monitor](http://s.alicdn.com/@sc04/kf/Hb10f67d5bd294f4eb39b44cf0b49edc6n.jpg_300x300.jpg)











































































































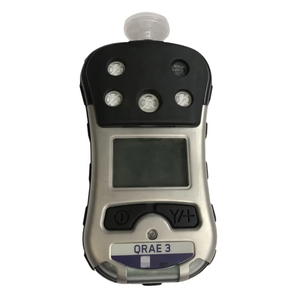























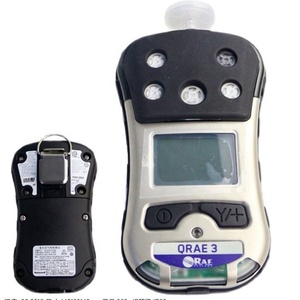





























A 3 1 gas detector can sense three gases at once and is helpful in many places, from factories to miners' underground work. It checks gas safety, helping people work safely and stopping explosions or poisonings.
Here are the types of a 3 1 gas detector:
Portable gas detectors
A portable gas 3 1 detector is small and moves easily. It checks gas levels in hard-to-get places or on the move. Coal miners use them to detect methane gas, which can cause explosions. Buildings use gas leak detectors to check for leaks while safely moving around. The tiny size and light weight make it easy to carry without wires.
Fixed gas detectors
Fixed gas detectors are placed in one spot and keep checking the air all the time. Factories use them to watch for dangerous gases like carbon monoxide or hydrogen. If the gas level gets too high, the alarm sounds to warn everyone. They help prevent fires, explosions, and sickness by spotting problems early. Since they always watch, they give workers peace that the plant is safe.
Multichannel gas detectors
A multichannel gas detector can check many gases at once. It uses sensors to scan for anything wrong. Industries that use solvents or chemicals need them to catch poisonous fumes like benzene. All the sensors give data to one place so people can see if any gas levels get too high. This helps stop sickness or danger by letting workers act fast before problems get worse.
Transmissive gas detectors
Transmissive gas detectors are systems that inspect how light acts in the presence of gas. As light travels through, the internal parts can tell which gas is within and its amount. This form excels in checking gases in pollution monitoring or lab work. It offers solid accuracy without needing much upkeep compared to older models.
Gas detectors help with safety by sensing dangerous gases and how at-risk workers can be. The tools must last long and work safely. In this piece, the materials and durability of a 3 1 gas detector are analyzed and explained.
Sensors
Sensors are the parts that feel the gas. Common types are catalytic beads, electrochemical cells, and infrared sensors. Catalytic beads work with wires that sense gas by creating heat. Electrochemical cells use chemicals and electrical currents to detect gas. Infrared sensors send light, which changes when gas is present.
Protective casing
The outer shell, known as the 'housing,' protects the internal parts. Plastics like polycarbonate form shields around fragile parts. Tougher cases made of metals like aluminum are also used in very tough settings such as mines or manufacturing plants where regular wear and tear can drastically damage the detector. Heavy-duty housings are created to endure trauma from dropping, water, and other dangers, so the instrument remains functional in tough settings. This ensures that the gas detector can continue working effectively even in the most extreme environments.
Water & dust proofing
Many 3-in-1 gas detectors can handle water and dust. They are rated IP65 or higher. This means they can survive getting wet or covered in dirt. Rubber seals called gaskets keep water out. They also keep out small bits of dirt or dust that could hurt the detector. This ensures the device performs reliably under various weather conditions.
Internal components
Wiring and circuit boards make the gas detector work. Good wiring ensures the parts can carry current without breaking. Fine circuit boards enable various components to work together. Dyes and other materials in these parts were chosen for their strength and resistance to environmental elements. They were prepared to survive internal heating and pressure, functioning for long spans without failing.
Mining operations
In mining, gas detectors find explosive gases like methane. Workers wear portable detectors to receive gas level readings. If dangerous gas is found, they will be alerted, so all can get to safety. Staying aware of gas presence helps miners keep working safely underground.
Oil & gas industries
Oil and gas workers use 3-in-1 detectors to find leaks and gas exposure. Detectors help them track hydrogen sulfide and other gases. The portable detector can be taken into the field and to well sites for immediate leak detection. Quick detection prevents sickness and explosions, keeping the area secure.
Emergency services
Emergency workers use gas detectors at fire scenes and rescues. The detector identifies explosive gas and dwindling oxygen. It keeps workers safe by revealing dangers in risky areas. Knowing gas levels in real time saves lives during risky events.
Confined space work
People working in tight spaces like tanks and tunnels rely on gas detectors. Before entry, detectors scan the air for toxic gas. While working, they give updates to ensure safe breathing. This use helps avoid suffocation or poisoning in cramped environments.
Industrial manufacturing
In factories, gas detectors track fumes from chemicals and machines. They keep watch for carbon monoxide and solvent vapors. Early warning gives workers time to act against hazards. This monitoring protects those working directly with dangerous materials.
Wastewater treatment plants
Gas detectors are used in treatment plants to find methane from waste breakdown. Detectors scan air around pits and tanks to give readings. Workers see risks before they get harmful. The equipment helps them finish work safely without gas dangers.
Chemical plants
Chemical plant workers depend on gas detectors to track fumes from production. Detectors mark gases like ammonia and hydrogen. They keep watch for leaks in real time. This detection acts quickly to prevent poisoning or explosions.
Assess gas exposure risks
Determine which gases might be present in the area. This guide is the first step to ensuring the right instrument is chosen for the task at hand. For example, a factory might have carbon monoxide, so it would need a detector for that. By knowing what gases come up, one can choose a gas leak detector that will safely cover all necessary bases.
Sensor types
Different sensors work better for different gases. Catalytic sensors are good for flammable gases, while electrochemical ones track toxic gases like hydrogen sulfide. Choosing the right kind for the specific tasks required helps boost accuracy and efficiency. Picking the inner parts that are appropriate will guarantee that the product will perform its essential functions properly.
Display & interface
The screens should be observable, and the buttons should be easy to use so that one can read the gas levels and settings without any issues. A simple interface allows the user to navigate without distraction, especially during emergencies. This is vital to ensure one can quickly gather all important information in any circumstance.
Portability vs. fixed
Decide whether a portable or fixed 3-in-1 gas detector is needed based on where it will be used. Portable ones are light and simple to move about, making them ideal for working in several locations. On the other hand, stationary detectors are set in one area and frequently supply constant gas monitoring. By weighing the requirements and applications, one can make an informed decision.
Durability
Make sure the detector can handle the work site. Get one that is water and dustproof if working outside. Bumps and drops are also a possibility, so choose a strong model. The gas 3-in-1 detector must last long in tough circumstances to ensure that monitoring stays in effect.
Battery life
Check how long the battery lasts, especially for portable models. One can't have a device that runs out of power when it's needed most. Select detectors with long battery lives or quick charging times to help with this problem. A reliable power source is simply critical for keeping operations running smoothly.
Watch for alarms
As gas levels change, the detector must sound alerts and give clear readings so everyone knows what is going on. One must select a product that will notify when there are risks. Because this function is key to allowing early action and thus promoting safety.
A1: A 3 gas detector tracks three gases at once using special sensors. It works by sending out tiny currents that change when gas is present. The sensor then reads these changes to tell how much of each gas is in the air. This is important for safety because it alerts workers if any gas levels get too high.
A2: The most important function is to spot dangerous gas levels and warn people. By doing this, it helps prevent risks to health and safety at work, such as fires or explosions. Just like that, it can keep an eye on air quality to ensure the environment is safe.
A3: The 3 1 gas detector is used by miners, factory workers, and any place with gas risks. Emergency crews and construction workers also use it. Waste plants, oil rigs, and places that work with chemicals rely on it for safety. Even power plants and labs use it to stay safe when working with gases.
A4: The main difference is what each one does. A gas detector looks for danger by sensing gases and warning about leaks. It helps keep people safe. A gas analyzer checks the air to identify and measure all kinds of gases, even safe ones. 3 In that way, it helps monitor air quality and track emissions.